Understanding Technical Rated Current in Motors
The technical rated current in motors is a vital parameter that directly affects motor performance and longevity. Exceeding the rated current can temporarily boost torque, but improper management risks overheating and motor damage. This article will guide you through essential concepts and practical tips to safely operate motors beyond their rated current.
What Is Technical Rated Current in Motors?
The technical rated current in motors refers to the maximum continuous current the motor can handle safely without overheating. It is defined by the manufacturer based on thermal limits of motor windings and insulation. Operating above this current is possible but requires strict control of duty cycles and cooling to prevent permanent damage.
Why Exceeding Rated Current Requires Caution
In many applications, engineers push motors beyond their rated current to gain higher torque output. However, continuous operation at such elevated currents leads to excessive temperature rise. This can degrade insulation, accelerate wear, and cause motor failure. Therefore, motors must not be operated continuously above their rated current without considering safe operating guidelines.
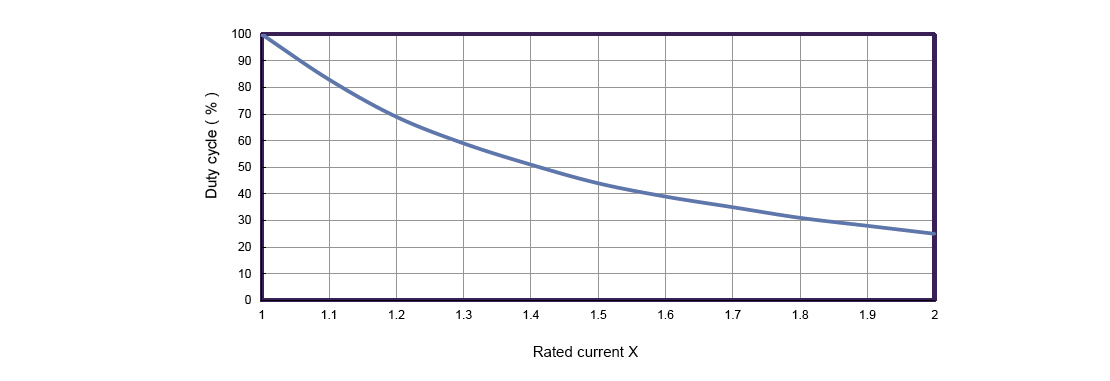
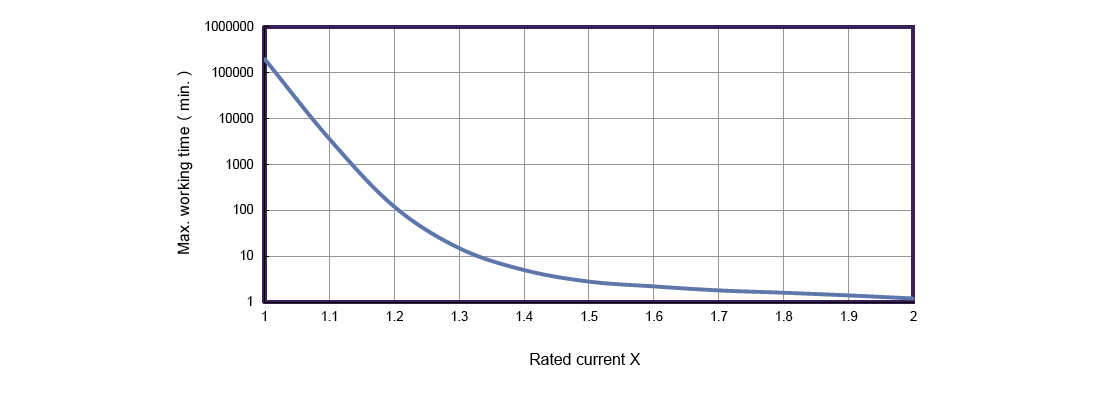
Duty Cycle and Maximum Operating Time (Ton Max)
When running motors above their rated current, it is essential to use a duty cycle less than 100%. The duty cycle refers to the ratio of operating time (Ton) to total cycle time (Ton + Toff). For example, a 50% duty cycle means the motor runs half the time and rests the other half.
Manufacturers provide duty cycle guidelines, including the maximum allowable single operating time (Ton Max) at different current levels. Adhering to these limits ensures the motor cools adequately between operation intervals, maintaining temperature within safe bounds.
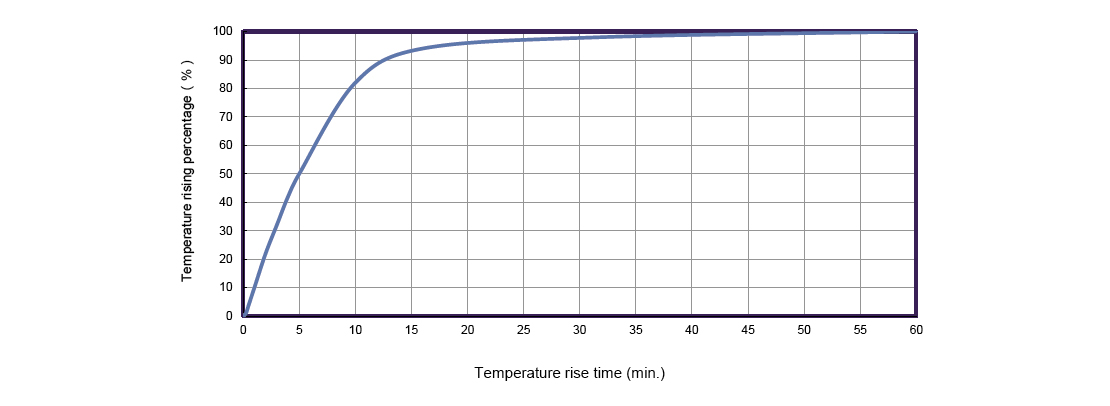
Temperature Rise and Its Impact on Motor Life
The temperature rise of motor windings is directly influenced by current magnitude and duty cycle. Typical temperature rise curves show how winding temperature increases over time under various current loads. Monitoring and managing this temperature rise is crucial to prevent insulation breakdown and extend motor life.
Practical Tips for Managing Technical Rated Current in Motors
Consult Manufacturer Specifications: Always refer to datasheets for rated current, duty cycle limits, and temperature rise curves.
Implement Duty Cycle Controls: Use timers or controllers to enforce rest periods (Toff) when operating above rated current.
Monitor Motor Temperature: Employ thermal sensors or use driver features that limit current based on temperature feedback.
Use Appropriate Cooling: Enhance heat dissipation with fans, heatsinks, or liquid cooling if operating near or above rated currents.
Avoid Continuous Overcurrent Operation: Limit high-current runs to short bursts within Ton Max to prevent damage.
Conclusion
Mastering the technical rated current in motors is key to achieving higher torque without compromising motor health. By understanding duty cycles, temperature rise, and adhering to manufacturer guidelines, you can safely push motor performance while ensuring longevity.
Recommended Articles:
Stepper Motor Step Angle and Calculation Formula: Complete Guide (2025)
Difference Between Sinking Current and Sourcing Current: 7 Powerful Facts
Motor Torque Calculation Formula: Simple Guide with 5 Key Torque Formulas
